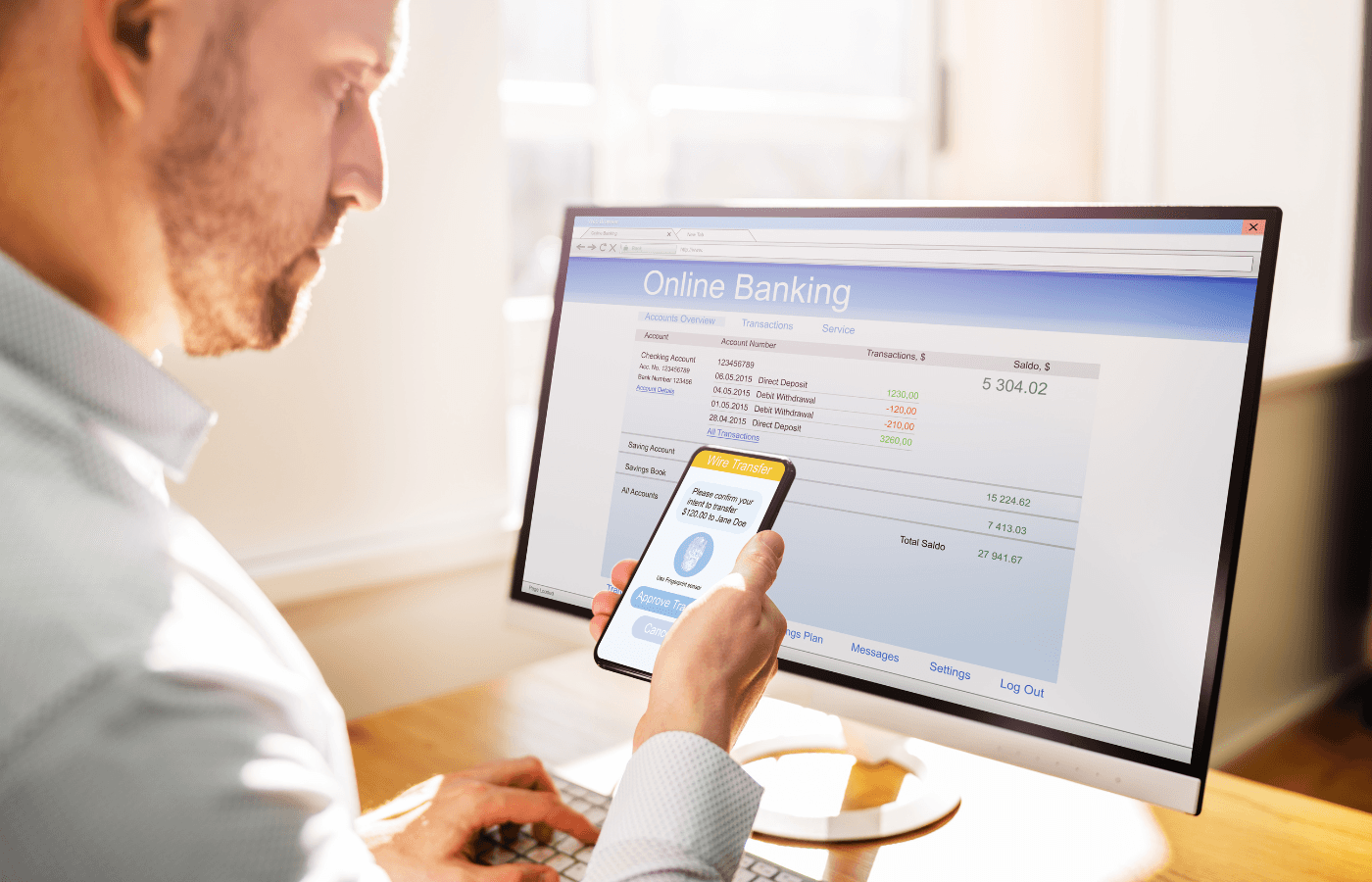
Huge portions of our lives are spent online. We use apps to shop, travel, remortgage homes, get appointments with our doctors — you name it. And although it makes life a lot easier in many respects, it also creates a wealth of opportunities for cybercriminals.
According to Consumer Reports' 2024 Consumer Cyber Readiness Report, 46% of Americans say they’ve recently been the target of an online scam or phishing attack. Almost half of those attacks started via email, and an increasing number of phishing attempts are coming out of WhatsApp, iMessage, and social networking channels.
Scammers are doing their best to work around two-factor authentication, or 2FA, and it’s getting harder to tell what’s genuine and to keep your online information safe.
However, there are strategies you can put into place to protect yourself and your family. That’s why we sat down for a Q&A session with Sam Riley, principal at Allixo.
Allixo is a Mount Vernon, Washington, SaaS and cybersecurity provider that specializes in supporting businesses to safeguard their digital assets and create fortified digital defenses. Over the past 15 years, Riley has guided Allixo from strength to strength, earning personal security certifications from Cisco and ISC2 along the way.
Read on to get Riley’s take on how 2FA has caused scammers to evolve, find out how the most common phishing scams work, and get tips on how to spot and avoid phishing scams.
What Is Phishing, and How Do Phishing Scams Work?
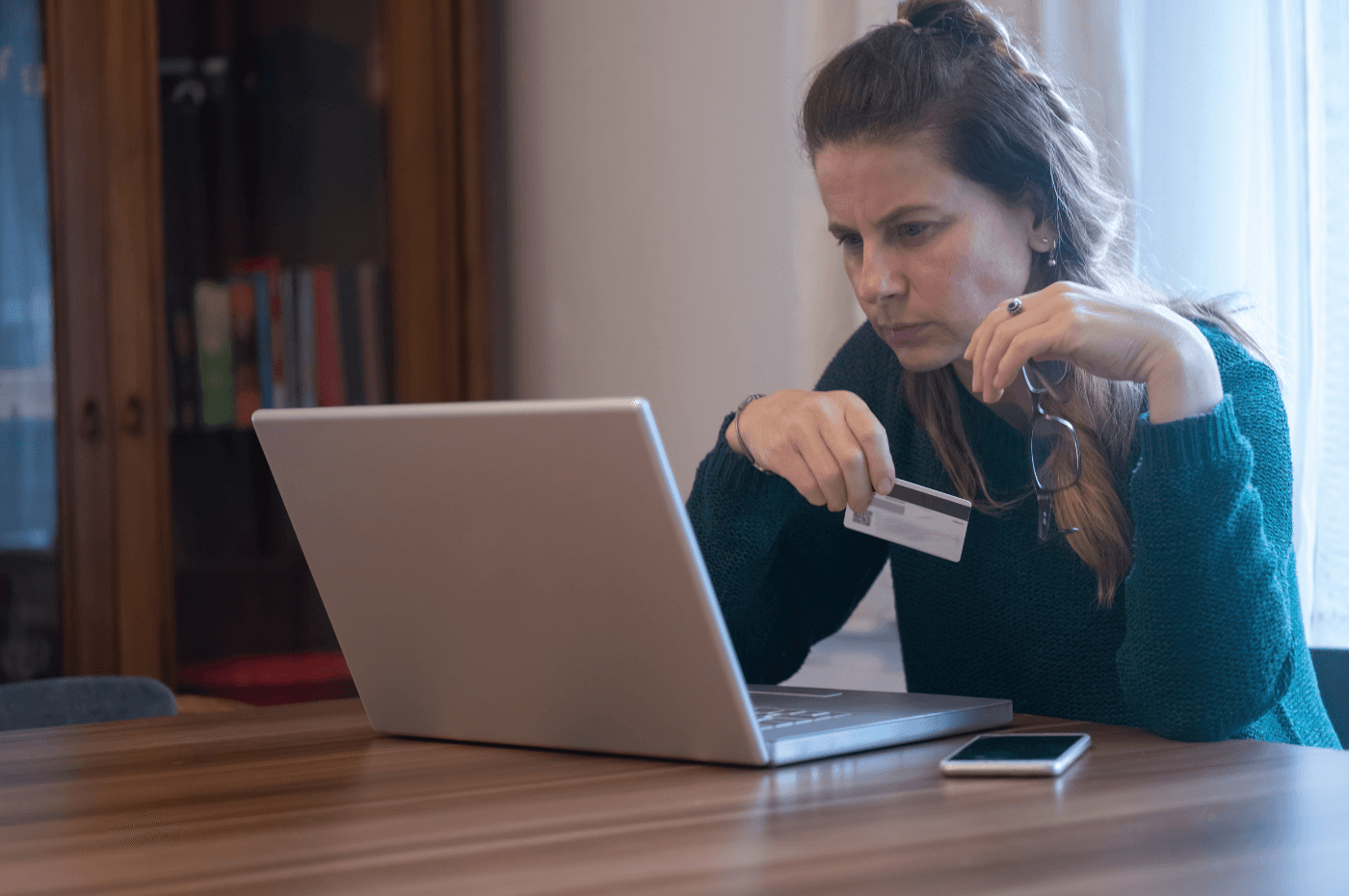

Answer: Phishing attacks take advantage of the weakest link in many cybersecurity postures, the end user.
Attackers use deceptive emails, messages, or websites to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information, such as login credentials or financial details.
These scams often involve creating fake websites or messages that closely mimic trusted entities, exploiting trust and urgency to lure victims into sharing their data.
How Has Two-Factor Authentication Changed Phishing?
Answer: A startling number of organizations still do not have 2FA fully implemented. Depending on the study you read, it may be as high as 50%.
When faced with picking targets, attackers often choose to focus on the low-hanging fruit with no 2FA. Even when 2FA is enabled, hackers have adapted by employing real-time phishing techniques. They now design sophisticated methods to intercept 2FA codes or lure victims into using fake portals that capture both passwords and authentication codes simultaneously.
The FBI recently released guidance that recommends discontinuing SMS-based 2FA.
Text messages are not encrypted by default, and both scammers and hostile state-sponsored attackers have started taking advantage of this. To help remedy this, we have moved towards eliminating text-based 2FA across our client base.
What Are Common Techniques Hackers Use to Steal 2FA Codes?
Answer: Attackers create fake login pages that mimic legitimate ones, tricking victims into entering their credentials and 2FA codes. Once the victim submits the code, the attacker uses it immediately on the real site, bypassing authentication in real time before the code expires.
Man-in-the-middle (MITM) tools like Evilginx act as intermediaries between the user and a legitimate website. When a victim logs in through a malicious link, the tool captures login credentials and 2FA codes while relaying them to the real website, granting the attacker full access.
We deploy both third-party tools and our own proprietary methods to warn a user if they have arrived at a site that is about to steal their information in this way.
One of the more concerning methods we have seen is when an attacker (or penetration tester) simply calls a user and pretends to be their IT company.
It is not always possible for them to determine which IT company to impersonate, but with a little sleuthing, they are often able to do so. If the user believes them, they’ll willingly start a remote session or other activity that completely bypasses 2FA. It is important for IT companies to protect their clients by having strict policies regarding when and how they contact users.
How Can Attackers Hijack Phone Numbers to Receive SMS-Based 2FA Codes?
Answer: A few years ago, when I called my cell phone carrier to transfer my phone number, they verified who I was with only easy-to-obtain information, like my address or phone model, and then proceeded to do everything I asked.
In recent years, carriers have become more secure, but attackers are still often successful in tricking or bribing telecom employees or using social engineering (not as difficult as it should be) to convince the carrier to transfer a victim’s phone number to a new SIM card under their control.
Once successful, they receive SMS-based 2FA codes intended for the victim, enabling unauthorized access.
What Are the Vulnerabilities in 2FA Methods?
Answer: 2FA that utilizes push notifications or one-time approvals rather than a code is susceptible to 2FA fatigue attacks, where a user is repeatedly sent 2FA requests until they press “Approve” out of habit.
SMS-based 2FA is vulnerable to SIM swapping, interception, and phishing. Authenticator apps are more secure but can be targeted through MITM attacks.
Hardware keys offer strong protection but may be inconvenient or costly for users. Biometrics are secure but susceptible to spoofing or data breaches if the biometric data is stolen.
How Can You Recognize and Avoid Phishing Scams Targeting 2FA?

Answer: Fake websites often have slight misspellings in the URL, lack SSL certificates (no padlock in the address bar), or use design elements that don’t match the legitimate site. Carefully inspecting the URL and avoiding links from unsolicited emails can help spot them.
Common red flags include poor grammar, spelling errors, generic greetings, suspicious sender addresses, urgent or threatening language, unexpected attachments, and requests for sensitive information. Hovering over links often reveals mismatched or strange URLs. When in doubt, always verify the sender using another means of communication.
Tools like anti-phishing browser extensions and security software can block malicious sites. Password managers also help by automatically filling in credentials only on verified domains, making phishing sites easier to identify.
What Steps Should You Take If Your 2FA Codes Have Been Compromised?
Answer: Immediately change passwords for the affected account and any linked accounts.
Revoke active sessions and reset 2FA settings to use a more secure method. Monitor for unauthorized activity and consider contacting the service provider to secure the account further.
If a mail account was compromised, check for forwarding rules that may have been created by the attacker.
What Advanced Security Do You Recommend to Protect Against 2FA Phishing?
Answer: Only a 2FA solution that enables both strong technical controls as well as effective user education will be secure in the long term.
Using hardware security keys like YubiKey or FIDO2-compliant devices is highly effective.
Enabling phishing-resistant authentication methods and endpoint security software, and ensuring employees undergo cybersecurity training can also significantly reduce risks.
What Does the Future Look Like for 2FA and Phishing-Resistant Solutions?
Answer: Technologies like Windows Hello for Business and passwordless authentication are reducing reliance on traditional 2FA by integrating biometrics and cryptographic keys. These methods eliminate the need for shared secrets like passwords, which are prone to phishing.
Phishing-resistant methods like WebAuthn, which leverages public-key cryptography, are gaining traction.
These methods ensure authentication is bound to specific devices and domains, making it nearly impossible for attackers to intercept or misuse credentials.
Related: Password Hygiene 101
–––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––
Keeping Your Data Secure Using Trustworthy
Here at Trustworthy, we understand that nothing is more important than preserving your data security — and we know that cybercriminals are getting sharper.
That’s why Trustworthy deploys bank-level security features to ensure you’re always protected from scammers. Trustworthy’s secure Family Operating System® enables you to upload and organize all your important family documents using one dynamic dashboard.
Trustworthy is SOC 2 Type 2 and SOC 3 certified, and it enables you to categorize passports, bank statements, insurance policies, tax returns, passwords, estate plans, and more.
That means your important documentation is always accessible and easy to find, but it’s always under lock and key.
Trustworthy combines two-factor authentication, hardware keys, and biometric (facial or fingerprint) authentication on our mobile app and on desktop to ensure your account is always 100% secure.
Everything you upload onto Trustworthy is protected using AES 256-bit encryption and tokenization — which removes sensitive data from the Trustworthy application database and replaces it with a corresponding token to keep your sensitive information protected and separate from your account.
Ready to discover Trustworthy for yourself? Sign up and get started for free.
We’d love to hear from you! Feel free to email us with any questions, comments, or suggestions for future article topics.
Trustworthy is an online service providing legal forms and information. We are not a law firm and do not provide legal advice.